Royal Tombs of Vergina
- The Antiquity of Aigai and its Archaeological Museum
- The Significance of the Tombs
- The Golden Treasures of Vergina
- The Murals of the Tombs
- The Archaeological Site of Aigai
- The History of Macedonia
- The Legacy of Alexander the Great
- The Modern City of Veria
- Planning Your Visit
- Getting There
- Where to Stay
- What to Eat
- What to Buy
- Insider Tip: Unveiling the Hidden Treasures of the Vergina Museum
The Antiquity of Aigai and its Archaeological Museum
The ancient city of Aigai, located near modern-day Vergina, was the first capital of the Kingdom of Macedon, a powerful state that emerged in the 4th century BC under the leadership of Philip II and his son, Alexander the Great. The city's strategic location in the fertile plains of Macedonia and its proximity to the sea made it a thriving center of trade and culture.
The Archaeological Museum of Vergina, situated in the heart of Vergina, houses a treasure trove of artifacts excavated from Aigai and other nearby sites. The museum's collection includes exquisite gold jewelry, intricately carved sculptures, and finely painted pottery, offering a glimpse into the artistry and craftsmanship of ancient Macedonia. Notable exhibits include the golden wreath found in Philip II's tomb, the ornate gold diadem worn by his wife, Cleopatra, and the stunning murals adorning the walls of the royal tombs.
The museum provides visitors with a comprehensive overview of Aigai's history and its role as the political and cultural center of the Macedonian kingdom. Guided tours are available to enhance the visitor experience and provide deeper insights into the significance of the artifacts on display. The museum's hours of operation and admission fees vary, so it is advisable to check the official website for up-to-date information.
The Significance of the Tombs
The royal tombs of Vergina hold immense historical significance, offering a glimpse into the opulent world of the Macedonian monarchy. These tombs, meticulously constructed and richly adorned, serve as a testament to the wealth and power of the Macedonian kingdom during the 4th century BC. The artifacts discovered within the tombs provide valuable insights into the burial customs and rituals of the ancient Macedonians, shedding light on their beliefs and practices surrounding death and the afterlife.
Beyond their historical importance, the royal tombs also possess immense artistic and cultural value. The exquisite craftsmanship and intricate designs of the artifacts reflect the influence of both Greek and Oriental traditions, showcasing the cultural diversity and cosmopolitan nature of the Macedonian kingdom. The golden treasures, with their intricate details and symbolism, offer a glimpse into the artistic prowess of ancient Macedonian goldsmiths, while the murals adorning the tomb walls depict scenes from Greek mythology and Macedonian history, providing a visual narrative of the kingdom's rich cultural heritage.
The Golden Treasures of Vergina
The royal tombs of Vergina yielded a breathtaking collection of gold jewelry and ornaments, showcasing the exceptional craftsmanship of ancient Macedonian goldsmiths. Among the most notable pieces is the golden larnax (casket) containing Philip II's remains. This intricately decorated casket features exquisite repoussé work depicting scenes from Greek mythology and Macedonian history. Another highlight is the golden diadem worn by Philip II's wife, Cleopatra. This stunning headdress is adorned with intricate floral motifs and precious gemstones, reflecting the opulence and status of the Macedonian royal family.
These golden treasures, along with other artifacts discovered in the tombs, provide valuable insights into the wealth and power of the Macedonian kingdom. They also shed light on the artistic and cultural influences that shaped Macedonian society, blending Greek and Oriental traditions. The golden treasures of Vergina are displayed in the Archaeological Museum of Vergina, where visitors can marvel at their beauty and historical significance. Strict security measures are in place to protect these priceless artifacts, ensuring their preservation for future generations.
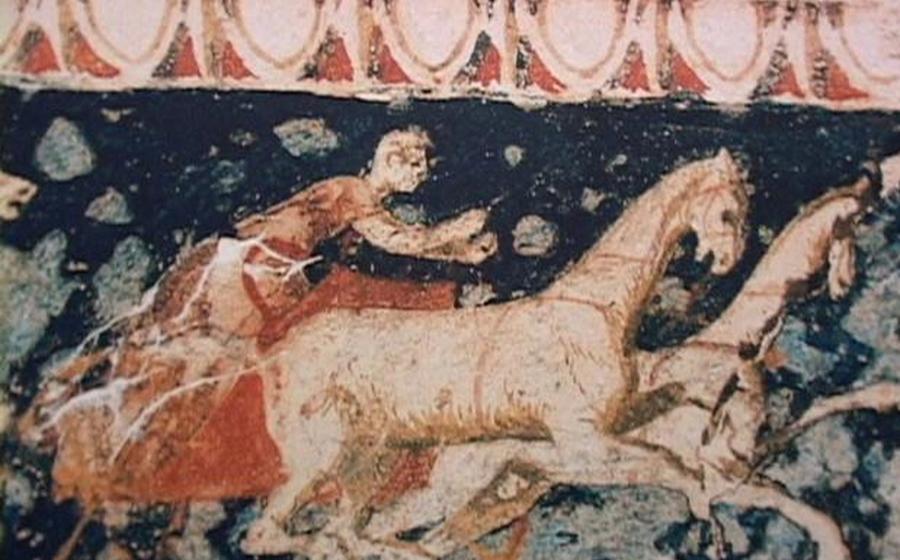
The Murals of the Tombs
The Royal Tombs of Vergina are adorned with exquisite murals that depict scenes from Greek mythology and Macedonian history. These murals, painted with vibrant colors and intricate details, offer a glimpse into the artistic and cultural traditions of the ancient Macedonians. One of the most famous murals is the "Abduction of Persephone," which portrays the god Hades abducting the goddess Persephone to the underworld. Another notable mural is the "Lion Hunt," which depicts a group of hunters pursuing a lion in a dramatic and dynamic scene.
The murals in the Royal Tombs of Vergina are not only visually stunning but also historically significant. They provide valuable insights into the religious beliefs, mythology, and artistic influences of the ancient Macedonians. The murals demonstrate the influence of both Greek and Persian art, reflecting the cultural diversity of the Macedonian kingdom.
The murals in the Royal Tombs have been carefully preserved and restored to ensure their longevity. Visitors can admire these masterpieces in their original context, gaining a deeper understanding of the ancient Macedonian civilization. However, due to their delicate nature, some of the tombs may have restricted access or viewing limitations to protect the murals from damage or fading.
The Archaeological Site of Aigai
The ancient city of Aigai, located near modern-day Veria, was the first capital of the Kingdom of Macedon, reigning from the 7th century BC until the rise of Pella in the 4th century BC. Today, visitors can explore the impressive archaeological site of Aigai, which offers a glimpse into the grandeur and history of this once-powerful city.
Among the highlights of the site are the remains of the royal palace, a vast complex that once served as the residence of the Macedonian kings. The palace features intricate mosaics, frescoes, and sculptures, showcasing the artistic achievements of ancient Macedonia. Another notable structure is the theater, which could accommodate up to 10,000 spectators and hosted performances of Greek plays and other events.
In addition, visitors can explore the bouleuterion (council chamber), where the Macedonian assembly met to discuss and decide on important matters of state. The archaeological site also includes temples dedicated to various deities, such as Zeus, Apollo, and Cybele, providing insights into the religious practices of the ancient Macedonians.
Ongoing excavations and research at the site continue to uncover new discoveries, shedding light on the daily lives, customs, and political systems of this ancient civilization. Visitors can learn more about the history and significance of Aigai through guided tours, informative signage, and interactive exhibits at the on-site museum.
The History of Macedonia
Macedonia, a region with a rich and storied past, traces its roots back to the ancient Greek tribes who settled in the area around the 8th century BC. Over time, the Macedonians emerged as a distinct people, developing their own unique culture and political system. The rise of the Kingdom of Macedon under Philip II in the 4th century BC marked a turning point in Macedonian history. Philip's ambitious military campaigns and innovative reforms transformed Macedonia into a formidable power, poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the course of ancient history.
During Philip's reign, the capital of Macedonia was moved from Aigai to Pella, a strategic location that facilitated the kingdom's expansion. Philip's son, Alexander the Great, inherited a vast and well-organized empire, which he would use to conquer much of the known world. Alexander's conquests not only spread Greek culture and influence throughout the Mediterranean region and beyond but also laid the foundation for the Hellenistic period, a transformative era marked by cultural exchange and innovation.
After Alexander's death, Macedonia faced a period of turmoil and division, with various factions vying for control. The kingdom eventually fell to the Romans in the 2nd century BC, becoming a province of the Roman Empire. During the Byzantine period, Macedonia remained an important province, with Thessaloniki serving as its administrative center. The region's strategic location made it a frequent target of invasions by various groups, including the Slavs, Bulgarians, and Normans.
In the 14th century, Macedonia came under Ottoman rule, which lasted for over 500 years. During this period, the region experienced a decline in its economy and culture. The Greek War of Independence in the 19th century led to the liberation of parts of Macedonia, but the region remained divided between Greece, Serbia, and Bulgaria. The Balkan Wars of 1912-1913 resulted in the incorporation of most of Macedonia into Greece, with smaller portions going to Serbia and Bulgaria.
Throughout its history, Macedonia has been a melting pot of cultures, with influences from Greek, Roman, Byzantine, Ottoman, and Slavic traditions. This rich heritage is reflected in the region's diverse architecture, cuisine, and customs. Today, Macedonia is a vibrant and dynamic region, known for its natural beauty, cultural attractions, and historical significance. Visitors to Vergina and the surrounding area have the opportunity to explore the fascinating history of Macedonia and gain insights into the lives and achievements of its ancient inhabitants.
The Legacy of Alexander the Great
Alexander the Great's conquests left an indelible mark on the ancient world, shaping the course of history and culture. His military prowess and strategic genius led to the creation of a vast empire that stretched from Greece to India, encompassing diverse lands and peoples. Alexander's campaigns not only brought political and territorial gains but also facilitated the spread of Greek culture, language, and ideas throughout the Mediterranean region and beyond.
The Hellenistic period, which followed Alexander's death, was characterized by a fusion of Greek and Eastern influences, resulting in a vibrant and cosmopolitan society. The cities founded by Alexander, such as Alexandria in Egypt, became centers of learning and culture, attracting scholars, artists, and philosophers from across the ancient world.
Alexander's legacy continues to fascinate and inspire people to this day. His life and achievements have been the subject of countless books, films, and documentaries, capturing the imagination of generations. The enduring debate surrounding his military strategies, leadership qualities, and the impact of his empire ensures that Alexander's legacy remains a topic of scholarly research and popular interest.
Practical Information:
- Visit the Archaeological Museum of Pella, Alexander's birthplace, to learn about his early life and the kingdom of Macedonia.
- Explore the Mount Athos monasteries in Greece, where Alexander is venerated as a saint and his icon is displayed.
- Read books such as "The Life of Alexander the Great" by Plutarch or "Alexander the Great" by Peter Green for a deeper understanding of his life and conquests.
- Watch documentaries like "Alexander the Great: The Man Who Would Be God" or "The World of Alexander the Great" for a visual exploration of his empire.
The Modern City of Veria
The modern city of Veria, located in the heart of Central Macedonia, is a blend of ancient history and modern charm. As you stroll through its vibrant streets, you'll encounter a rich tapestry of cultures and traditions that have shaped this city over centuries.
Visit the picturesque Jewish Quarter, where you can explore the fascinating history of Veria's Jewish community and admire the well-preserved synagogues. Don't miss the vibrant central market, a hive of activity where locals and visitors alike come to shop for fresh produce, traditional delicacies, and handmade crafts.
Veria's Byzantine churches are architectural masterpieces that showcase the city's rich religious heritage. Marvel at the intricate frescoes and mosaics that adorn these sacred spaces, transporting you back in time to a bygone era.
Immerse yourself in the local customs and traditions that make Veria unique. Attend the annual "Anastenaria" fire-walking festival, a thrilling spectacle where barefoot dancers perform a ritual dance on burning coals. This ancient tradition, deeply rooted in local folklore, is a testament to Veria's enduring cultural heritage.
Practical Information:
- Accommodation: Veria offers a range of accommodation options, from budget-friendly guesthouses to luxurious hotels.
- Dining: Savor traditional Macedonian cuisine at local tavernas, where you can indulge in hearty dishes such as "kleftiko" (slow-cooked lamb) or "moussaka" (eggplant and potato casserole).
- Transportation: Veria is well-connected by public transportation, making it easy to explore the city and its surroundings. The city is also a popular destination for organized tours from major cities in Greece.
Planning Your Visit
Timing your visit to Vergina is crucial for a seamless experience. The best period to explore the Royal Tombs and the Archaeological Museum is during the shoulder seasons (spring and autumn) when the weather is pleasant, and tourist crowds are manageable. Summer months can be scorching, and the site is often packed with visitors, making it challenging to fully appreciate the exhibits.
Allocate at least half a day to explore the archaeological site and the museum thoroughly. Start your day early to beat the heat and crowds, especially if visiting during the summer. Guided tours are available in various languages and offer an in-depth understanding of the site's history and significance. Consider booking a tour in advance, particularly during peak season, to secure your spot.
For an immersive experience, consider hiring a local guide. They can provide fascinating insights into the history of Vergina and the surrounding region, bringing the ancient world to life. Local guides are often passionate about their heritage and can share unique stories and anecdotes that enhance your visit.
Getting There
Vergina is easily accessible by car, public transportation, or organized tour from major cities in Greece.
By car: From Thessaloniki, take the A2 motorway towards Veria. Exit at the Vergina/Aigai exit and follow the signs to the archaeological site. The drive takes approximately 1 hour and 30 minutes.
By public transportation: From Thessaloniki, take the train to Veria. The journey takes about 1 hour and 15 minutes. From Veria, take a bus or taxi to the archaeological site.
By organized tour: Many tour operators in Thessaloniki offer day trips to Vergina. These tours typically include transportation, a guided tour of the archaeological site and the museum, and lunch.
The nearest airport to Vergina is Thessaloniki International Airport (SKG). From the airport, you can take a taxi or bus to Veria. The journey takes about 1 hour.
Once in Vergina, there is ample parking available near the archaeological site. There is also a small parking lot at the museum.
For those with disabilities or special needs, there are accessible parking spaces available at the archaeological site and the museum. There are also ramps and elevators to make it easier to get around.
Where to Stay
When choosing accommodation in Veria, there are several factors to consider, including proximity to the archaeological site, budget, and desired amenities. For those seeking convenience, staying near the archaeological site offers easy access to the Royal Tombs and the Archaeological Museum. Several hotels and guesthouses are located within walking distance, providing a range of options from budget-friendly to mid-range.
For a more immersive experience, consider staying in the historic center of Veria, where you can wander through the charming streets, visit Byzantine churches, and sample local delicacies at traditional tavernas. This area offers a variety of accommodation options, including boutique hotels housed in restored mansions and cozy guesthouses with a local touch.
If you prefer a luxurious stay, Veria boasts several upscale hotels that offer modern amenities, elegant rooms, and personalized service. These hotels are often located in prime locations, providing stunning views of the city or the surrounding mountains.
No matter your budget or preferences, Veria offers a diverse range of accommodation options to suit every traveler's needs. Remember to book your stay in advance, especially during peak tourist season, to secure the best rates and availability.
What to Eat
In Veria, indulging in the culinary delights of the region is a must. Macedonian cuisine, with its rich flavors and hearty dishes, is sure to tantalize your taste buds. Start your culinary journey with the signature dish of the region, "giatoudi," a tender lamb stew cooked to perfection in a traditional clay pot.
For a taste of local delicacies, try the "bougatsa," a flaky pastry filled with cheese, spinach, or minced meat. Another must-try is "tourloumpouki," a vegetable stew featuring seasonal produce and a burst of flavors.
Vegetarians and vegans will find plenty of options to satisfy their cravings. "Fasolada," a hearty bean soup, is a staple in Greek cuisine and is sure to warm you up on a chilly day. "Gemista," stuffed vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, and zucchini, offer a delightful mix of flavors and textures.
To satisfy your sweet tooth, indulge in "loukoumades," delicious honey-dipped doughnuts, or "galaktoboureko," a creamy custard pie topped with crispy filo pastry. For a refreshing treat, try "kaymaki," a thick, creamy yogurt with a unique tang.
Local markets and street vendors offer a tempting array of fresh produce, nuts, and traditional sweets. Don't miss the chance to sample these culinary treasures and immerse yourself in the vibrant food culture of Veria.
What to Buy
In Vergina and Veria, you'll find a treasure trove of unique souvenirs and handicrafts that reflect the region's rich history and culture. Support local artisans and the economy by purchasing handmade pottery, intricate jewelry, and colorful textiles from the local markets, shops, and boutiques.
The central market in Veria is a vibrant hub of activity where you can browse stalls selling everything from fresh produce and spices to handmade crafts. Haggling is not only acceptable but expected, so don't be afraid to negotiate for the best price.
For a truly unique souvenir, visit the Vergina Gold Museum Shop, located near the Archaeological Museum. Here, you can find replicas of the exquisite gold artifacts discovered in the royal tombs, allowing you to take a piece of ancient Macedonian history home with you.
When shopping in Vergina and Veria, keep an eye out for traditional Macedonian clothing, such as the "fustanella," a pleated skirt worn by men, and the "poukamisa," a long-sleeved blouse worn by women. These garments are often adorned with intricate embroidery and colorful patterns, making them a beautiful and authentic souvenir.
No matter what you choose to buy, make sure to do your research and support local businesses that are committed to preserving the region's cultural heritage.
Insider Tip: Unveiling the Hidden Treasures of the Vergina Museum
As you wander through the halls of the Archaeological Museum of Vergina, keep an eye out for the exquisite gold jewelry and intricate artifacts displayed in glass cases. While the museum's star attractions are undoubtedly the treasures from the royal tombs, the lesser-known collection of gold jewelry from the Vergina Treasure is equally captivating. These delicate pieces, crafted with exceptional skill and artistry, offer a glimpse into the opulence and sophistication of ancient Macedonian craftsmanship. Don't miss the chance to admire the intricate gold earrings, necklaces, and bracelets that adorned the wealthy and powerful citizens of Vergina, providing a tangible connection to the grandeur of this ancient kingdom.