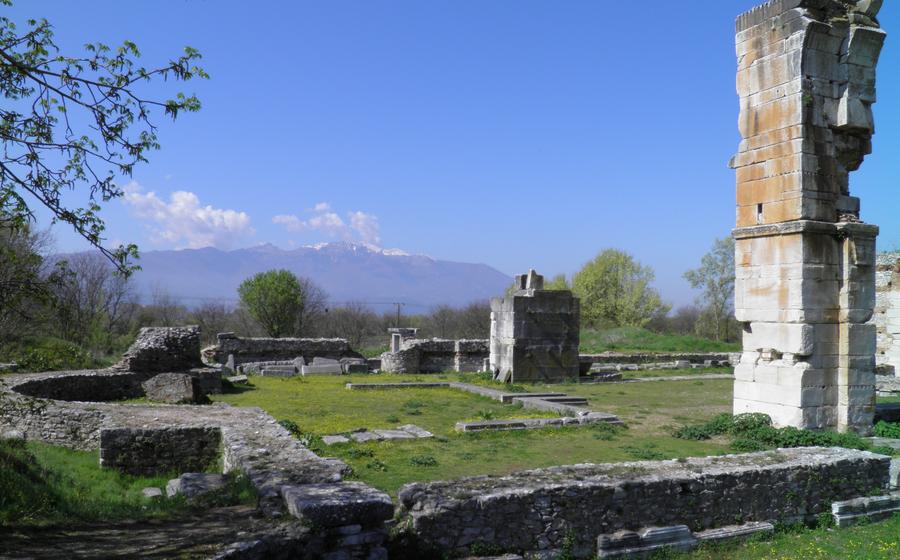
The Forum and Basilica of Philippi
- The Forum and Basilica of Philippi: A Journey Through Time
- Stepping into the Ancient Agora
- Exploring the Ancient Market: A Hub of Commerce
- The Via Egnatia: A Gateway to the Roman Empire
- Witnessing the Ancient Theater: Drama and Spectacles
- Discovering the Octagonal Church: A Unique Architectural Gem
- Unearthing the Baptistery: Rituals of Purification
- Exploring the Episcopal Basilica: A Center of Religious Authority
- The Hellenistic Wall: A Fortification of Ancient Philippi
- The Acropolis of Philippi: A Place of Worship and Power
- The Nymphaeum: A Place of Refreshment and Worship
- The Tomb of Lydia: A Touching Tribute to a Beloved Companion
- Insider Tip: Experience the Vibrant Local Culture
The Forum and Basilica of Philippi: A Journey Through Time
The Forum and Basilica of Philippi stand as testaments to the city's rich history and its pivotal role in the spread of Christianity. Excavations at the site have uncovered the remains of an impressive forum, the heart of ancient Philippi's public life, and a grand basilica, a symbol of early Christianity's growth and influence in the region.
Historical Significance: Philippi, founded by Philip II of Macedon in 356 BC, served as a strategic military outpost and a vital trade center. The city flourished under Roman rule, becoming a prominent member of the Roman Empire's eastern provinces. The forum, constructed in the 1st century AD, served as the city's administrative and commercial hub, hosting markets, political gatherings, and judicial proceedings.
Architectural Features: The forum's impressive colonnaded walkways, shops, and public buildings reflected Philippi's prosperity and importance. The basilica, built in the 5th century AD, showcased the grandeur of early Christian architecture with its three naves, intricate mosaics, and marble columns. Its size and elaborate design testified to the growing influence of Christianity in the city.
Excavations and Discoveries: Extensive excavations conducted at the site have brought to light numerous artifacts, including inscriptions, statues, and pottery shards. These findings have shed light on Philippi's history, economy, and daily life. The discovery of Christian symbols and inscriptions within the basilica further confirms the city's role as a center of early Christian activity.
Importance in Early Christianity: The Basilica of Philippi holds particular significance in the history of Christianity. It is believed to be the site where the Apostle Paul delivered his famous sermon, leading to the conversion of Lydia, a local businesswoman, and the establishment of the first Christian community in Europe. The basilica, with its impressive size and elaborate decoration, served as a place of worship, gathering, and religious instruction for the early Christian community.
Stepping into the Ancient Agora
The agora, the heart of Philippi's public life, was a bustling hub of activity in ancient times. It served as a marketplace, a gathering place for political debates and social interactions, and a venue for religious ceremonies. The agora's rectangular shape, surrounded by colonnaded stoas, created a spacious and orderly environment.
Excavations have revealed the remains of various buildings and structures that once lined the agora. These include shops and stalls where merchants sold their wares, administrative offices, temples dedicated to various deities, and even a mint where coins were produced. Numerous artifacts, such as pottery, tools, and inscriptions, have also been discovered, providing valuable insights into the daily life and economy of ancient Philippi.
The agora played a crucial role in shaping the social and political fabric of the city. It was here that citizens met to discuss important issues, make decisions, and elect their representatives. The agora was also a place of entertainment, where people could attend theatrical performances, listen to poets and philosophers, or simply relax and socialize.
By exploring the ancient agora of Philippi, visitors can gain a deeper understanding of the vibrant and dynamic life that once took place in this important city. It offers a glimpse into the political, economic, and social systems of the ancient Greek world and highlights the agora's significance as a central gathering place for citizens to conduct business, engage in civic life, and celebrate their shared culture.
Exploring the Ancient Market: A Hub of Commerce
In the bustling city of Philippi, the ancient market served as a vibrant hub of commercial activity. As you step into the unearthed remains of this marketplace, you embark on a journey through time, discovering the economic and social dynamics of this ancient city.
The market's strategic location along the Via Egnatia, a major trade route connecting the Roman Empire, made it a focal point for merchants and traders from across the region. Excavated shops and stalls line the streets, each offering a glimpse into the diverse goods that were exchanged in this bustling marketplace.
From locally produced agricultural products to imported luxuries, the market was a place where people came to buy and sell everything they needed. Farmers brought their freshly harvested crops, while potters displayed their intricately designed ceramics. Merchants from far-off lands showcased exotic spices, silks, and precious stones, creating a vibrant tapestry of sights, sounds, and aromas.
As you explore the excavated ruins, you can almost hear the lively chatter of shoppers haggling over prices, the clinking of coins, and the laughter of merchants as they closed deals. The market was not just a place of commerce but also a social gathering spot, where people came to meet, exchange news, and catch up on the latest gossip.
The Via Egnatia: A Gateway to the Roman Empire
The Via Egnatia, a sprawling network of roads, served as a crucial artery connecting the diverse regions of the Roman Empire. Constructed under the guidance of the Roman statesman Gnaeus Egnatius, this engineering marvel stretched over 500 miles, linking the Adriatic Sea to the shores of the Black Sea. Its strategic significance lay in its role as a conduit for trade, communication, and military movement, facilitating the seamless flow of goods, ideas, and armies across the vast empire.
The construction of the Via Egnatia was a testament to Roman engineering prowess. The road's meticulous design and construction ensured its durability and longevity, allowing it to withstand the wear and tear of constant use. Milestones and markers strategically placed along the route provided guidance to travelers, indicating distances and directions to major cities and settlements.
The Via Egnatia played a pivotal role in connecting the Roman Empire, fostering cultural exchange, and enabling the spread of Roman influence and power. It facilitated the movement of troops, allowing the Roman army to swiftly respond to threats and maintain control over its far-flung territories. Additionally, the road served as a conduit for trade, stimulating economic growth and prosperity in the regions it traversed.
Witnessing the Ancient Theater: Drama and Spectacles
The ancient theater of Philippi stands as a testament to the city's vibrant cultural life. Constructed in the 4th century BC, this impressive structure could accommodate up to 6,000 spectators. Its well-preserved stage, orchestra, and seating areas offer a glimpse into the world of ancient Greek entertainment.
During its heyday, the theater hosted a variety of performances, including plays, musical concerts, and gladiator fights. The acoustics are remarkable, ensuring that every word spoken on stage could be heard throughout the auditorium. The theater's strategic location on a hilltop provided stunning views of the surrounding countryside, enhancing the overall experience for spectators.
Excavations at the site have revealed intricate stage decorations, elaborate costumes, and musical instruments, providing valuable insights into the theatrical traditions of ancient Greece. The theater's remarkably preserved condition makes it one of the best-preserved ancient theaters in the world, offering visitors a unique opportunity to step back in time and experience the grandeur of ancient Greek drama.
Discovering the Octagonal Church: A Unique Architectural Gem
The Octagonal Church, a remarkable architectural gem nestled amidst the ruins of Philippi, stands as a testament to the city's rich history and diverse religious heritage. Its unique octagonal shape, a rarity in early Christian architecture, sets it apart from the other structures in the ancient city.
Constructed during the 5th century AD, the church showcases exceptional craftsmanship and innovative design. Its walls, composed of alternating layers of stone and brick, demonstrate the builders' mastery of construction techniques. The octagonal layout, with its eight sides radiating from a central point, creates a harmonious and visually striking interior space.
Excavations conducted at the site have revealed intricate mosaics and decorative elements that once adorned the church's interior. Geometric patterns, floral motifs, and biblical scenes come together to create a vibrant and colorful spectacle, offering a glimpse into the artistic traditions of the early Christian era.
The Octagonal Church holds immense significance in the history of early Christian architecture. Its unique design and construction techniques set a precedent for future church buildings, influencing the development of Byzantine and Romanesque architecture. The church's octagonal shape symbolizes the perfection and eternity of God, representing the heavenly realm and the divine presence within the earthly structure.
As you explore the ruins of Philippi, make sure to visit the Octagonal Church and marvel at its architectural brilliance. Its unique shape and intricate decorations provide a fascinating glimpse into the religious beliefs and artistic expressions of the ancient world.
Unearthing the Baptistery: Rituals of Purification
Within the sprawling ruins of Philippi, the ancient baptistery stands as a testament to the city's rich Christian heritage. This sacred space, dedicated to the ritual of baptism, holds profound significance in understanding the early Christian community's practices and beliefs.
The baptistery's architectural features are a testament to its importance. Its well-preserved design showcases a central baptismal font, an essential element for the immersion ritual. The surrounding area is adorned with intricate mosaics and decorative elements, creating an atmosphere of reverence and spirituality.
Excavations at the baptistery have unearthed a wealth of artifacts that shed light on the rituals performed within its walls. Baptismal fonts, adorned with symbolic motifs, provide tangible evidence of the baptismal practices that took place here. Mosaics depicting scenes of baptism offer a glimpse into the spiritual journey undertaken by those who sought purification and renewal.
The baptistery's role in early Christian rituals was pivotal. As a center for baptism, it served as a gateway for individuals to join the Christian community. Through the act of immersion, believers symbolically washed away their sins and embraced a new life in Christ. The baptistery thus stands as a symbol of spiritual transformation and regeneration, a place where the faithful embarked on a path of discipleship.
Exploring the Episcopal Basilica: A Center of Religious Authority
The Episcopal Basilica, with its imposing presence, stands as a testament to Philippi's religious significance in ancient times. Its grandeur and architectural features speak volumes about its importance as a center of Christian authority. Excavations have unearthed exquisite mosaics, frescoes, and inscriptions that provide valuable insights into the basilica's history and religious functions.
As you step through the basilica's grand entrance, you'll be awestruck by its sheer size and intricate design. The basilica's three naves are separated by rows of marble columns, creating a sense of spaciousness and grandeur. The central nave, adorned with intricate mosaics depicting biblical scenes, leads your gaze towards the apse, where the bishop's throne once stood.
The excavated mosaics and frescoes that adorn the basilica's walls and floors are a true testament to the artistic prowess of early Christian artisans. These vibrant and well-preserved mosaics depict various biblical scenes, including the life of Christ, the miracles he performed, and the teachings of the apostles. The vivid colors and intricate details of these mosaics bring the stories of the Bible to life, offering a glimpse into the beliefs and practices of the early Christian community.
Inscriptions found within the basilica provide valuable information about its construction, dedication, and the bishops who served there. These inscriptions reveal the names of the bishops who oversaw the basilica's construction and the dates of their tenure. They also shed light on the basilica's role in the spread of Christianity throughout the region, as it served as a center for religious authority and a place of worship for the faithful.
Exploring the Episcopal Basilica is a journey through time, allowing you to connect with the early Christian community and witness the grandeur of their religious practices. Its well-preserved mosaics, frescoes, and inscriptions offer a glimpse into the beliefs, rituals, and traditions that shaped the development of Christianity in this ancient city.
The Hellenistic Wall: A Fortification of Ancient Philippi
Philippi's Hellenistic wall, a testament to the city's resilience and strategic importance, stands as a reminder of its rich past. Constructed during the Hellenistic period, likely in the 4th century BC, the wall served as a protective barrier against invaders and ensured the city's security. Its massive stone blocks, carefully fitted together without the use of mortar, showcase the remarkable engineering skills of the ancient Greeks.
Excavations have revealed significant sections of the wall, providing valuable insights into its construction techniques and defensive features. The wall's thickness, ranging from 2 to 3 meters, and its height, estimated to have reached 10 meters, demonstrate its impressive scale and strength. Towers and gates strategically positioned along the wall allowed for surveillance and controlled access to the city.
The Hellenistic wall not only served a defensive purpose but also played a crucial role in defining Philippi's urban layout. It encircled the city, demarcating its boundaries and shaping its urban fabric. The wall's presence influenced the development of neighborhoods, public spaces, and infrastructure within the city walls.
Exploring the remains of the Hellenistic wall offers a glimpse into Philippi's strategic significance and its ability to withstand attacks and invasions throughout its history. It stands as a testament to the ingenuity and resilience of the ancient Greeks, who constructed remarkable fortifications to protect their cities and ensure their prosperity.
The Acropolis of Philippi: A Place of Worship and Power
Perched atop a hill overlooking the ancient city of Philippi, the acropolis stands as a testament to the city's rich history and religious significance. Its strategic location provided a commanding view of the surrounding area, making it an ideal spot for a fortified settlement. Excavations have revealed the remains of temples, altars, and other religious structures, indicating the acropolis's role as a center of worship and power.
The most prominent structure on the acropolis is the Temple of Athena Polias, dedicated to the patron goddess of the city. Its imposing columns and well-preserved pediments showcase the architectural prowess of the ancient Greeks. Other notable structures include the Temple of Zeus Hypsistos, dedicated to the supreme god of the Hellenistic pantheon, and the Heroon, a shrine dedicated to a local hero or ruler.
Beyond its religious significance, the acropolis also played a crucial role in the city's governance. It served as the seat of the city council and the assembly, where important decisions were made and laws were enacted. The acropolis was truly the heart of Philippi, a place where the spiritual and temporal powers converged.
As you explore the acropolis, take a moment to soak in the breathtaking views from its summit. The sprawling landscape of Philippi unfolds before you, with the Aegean Sea shimmering in the distance. It's easy to imagine the ancient Greeks standing on this very spot, surveying their domain with pride and reverence.
The Nymphaeum: A Place of Refreshment and Worship
Nestled amidst the ruins of Philippi, the Nymphaeum stands as a testament to the ancient city's devotion to the nymphs, mythological beings associated with water and nature. This sacred fountain served as a gathering place for the citizens of Philippi, offering respite from the scorching sun and a place to pay homage to these benevolent deities.
The Nymphaeum's architectural features exude an air of elegance and grandeur. Its intricate design includes a series of niches and alcoves, each adorned with exquisite statues depicting nymphs and other mythological figures. The fountain's central basin, where water once flowed freely, is surrounded by a mosaic floor that has been beautifully preserved, showcasing intricate patterns and vibrant colors.
Excavations at the Nymphaeum have unearthed a wealth of artifacts and inscriptions, providing valuable insights into the religious practices and beliefs of the ancient Philippians. Statues, votive offerings, and inscriptions dedicated to the nymphs have been discovered, shedding light on the significance of this sacred site.
The Nymphaeum's primary function was to provide a place for the citizens of Philippi to access fresh water, a vital resource in ancient times. However, it also served as a place of worship and devotion, where people could gather to honor the nymphs and seek their blessings. The presence of the fountain in the heart of the city underscores the importance of water in both the practical and spiritual aspects of ancient Greek life.
The Tomb of Lydia: A Touching Tribute to a Beloved Companion
In the heart of Philippi's ancient ruins, a poignant reminder of love and remembrance awaits discovery—the Tomb of Lydia. Unearthed during excavations, this exquisitely preserved tomb stands as a testament to the enduring bonds between humans and their companions.
Dating back to the 4th century BC, the tomb's discovery in 1954 unveiled a wealth of insights into ancient Greek funerary practices and the profound emotional connections shared between individuals. The tomb's most striking feature is its intricate bas-relief carvings, which depict scenes of everyday life and poignant farewells between a man and his beloved dog, Lydia.
The artistry and attention to detail in these carvings suggest that Lydia was not just a pet but a cherished companion, whose memory was honored with the utmost care and affection. The tomb's interior reveals further evidence of this devotion, with inscriptions and offerings expressing the owner's enduring grief and longing for his faithful friend.
As visitors stand before the Tomb of Lydia, they are transported back in time, witnessing the profound bonds that transcended the boundaries of life and death in ancient Greece. This touching tribute to a beloved companion serves as a reminder of the enduring power of love and the deep connections we forge with our animal companions.
Insider Tip: Experience the Vibrant Local Culture
To fully immerse yourself in the charm of Kavala, delve into the vibrant local culture. Stroll through the traditional markets, where you can find an array of fresh produce, handcrafted souvenirs, and local delicacies. Indulge in the delectable cuisine, savoring the flavors of traditional Greek dishes prepared with fresh, local ingredients. Engage with the friendly locals, who are always eager to share stories and insights into their customs and way of life. Don't miss the opportunity to attend cultural events and festivals, where you can witness traditional dances, music, and art, allowing you to experience the region's rich heritage firsthand. Embrace the warmth and hospitality of Kavala's people, and let their infectious energy enhance your journey, creating lasting memories of your time in this captivating city.